What is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic disease that affects the lungs. It occurs when the airways narrow, making it difficult to breathe. Although there is no cure for asthma, symptoms can be controlled with proper clinical treatment, appropriate use of medication, self-management education, and limited exposure to environmental triggers.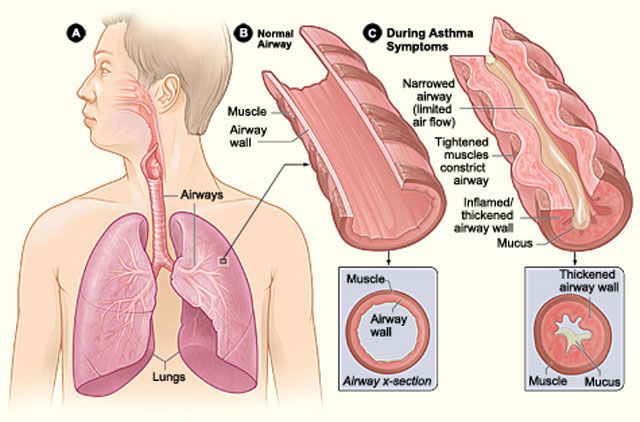
Asthma affects approximately 25 million people (including over 4.6 million children under the age of 18) in the US.[1]
Asthma is one of the most common chronic childhood diseases both in the United States and in Hawai‘i. When not effectively managed, people often seek treatment which drives up emergency department (ED) visits and hospitalizations, and their associated costs to the health care system, as well as negatively impacts school and work attendance and quality of life. Infants and young children (0 to 4 years of age) make up the majority of ED visits and hospitalizations due to asthma.[2,3]
Despite ongoing and targeted public health efforts to reduce the burden of asthma in Hawaiʻi, asthma-related health disparities persist. In 2022, Native Hawaiian adults (15.6%) were 1.7 times more likely to currently have asthma compared to the state average (9.1%).[4] Current asthma prevalence among Native Hawaiian children (11%) was higher than the state average (9.2%) in 2022.[2] Male children are more likely to have asthma than female children. This trend reverses in adulthood, where female adults are more likely to have asthma. Obesity is also a risk factor for asthma (i.e., the development of asthma, worsening asthma symptoms, and poor asthma control), and secondhand smoke is unhealthy for everyone, but particularly people with asthma.[3,5]
Learn more about Hawai’i asthma objectives and strategies in the Hawai‘i Asthma Plan 2030.
Sources:
[1] CDC: Asthma Surveillance in the United States,2001–2021.
[2] Hawaii State Department of Health, HHDW – Asthma Tracker. (BRFSS, 2022).
[3] Healthy Hawaii Strategic Plan 2030: Hawaii Asthma Plan.
[4] HHDW – Hawaii IBIS. (BRFSS, 2022). Crude rate.
[5] CDC NCHS Data Brief No. 239, March 2016. (2001–2014).



