Metals
Air | Ash and Debris | Beach Sand | Coastal Sediment | Coastal Waters | County Parks | West Maui TDS Site | Soil
Maui Wildfire Data: Air
Metals in Lahaina
Community air monitoring took place in late 2023, 2024, and early 2025. Monitoring was completed February 19, 2025. Data are available below.
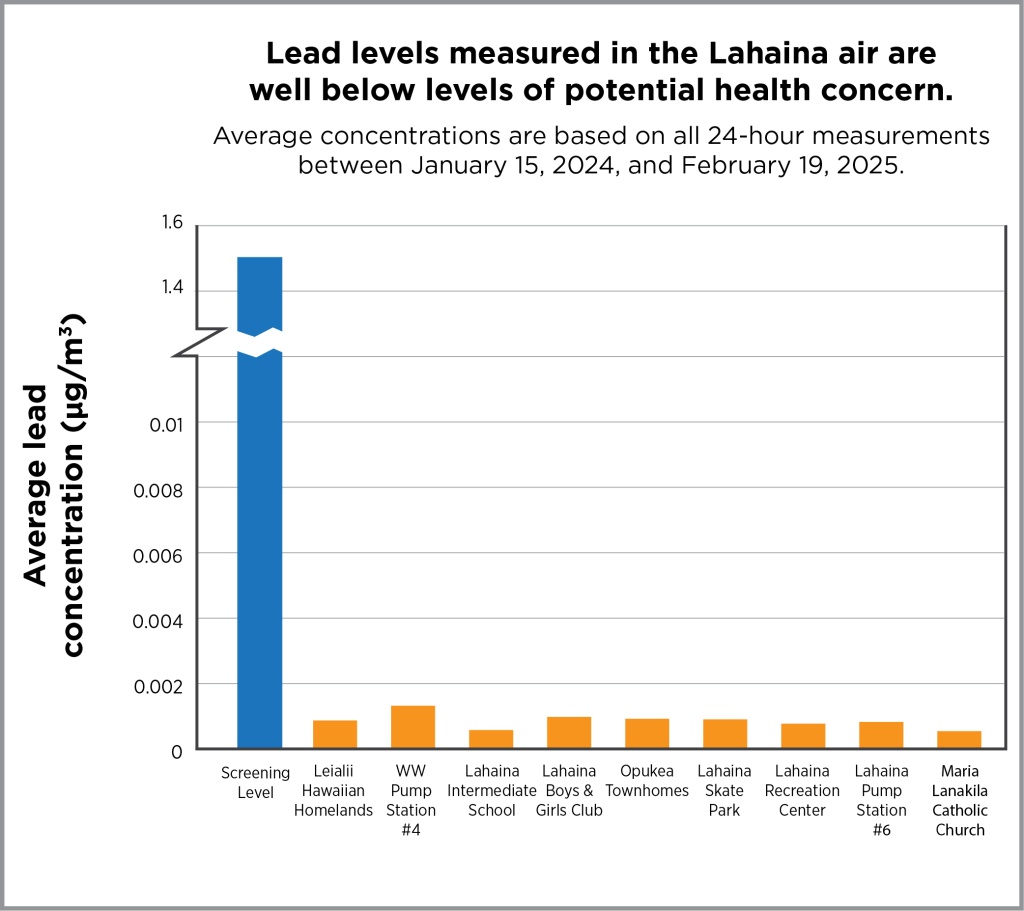
DOH has collected daily samples of airborne particles and tested them for harmful substances. This sampling began on January 15, 2024, before debris removal activities started, and ended on February 19, 2025, after debris removal from Lahaina properties was complete. The samples were collected at the Lahaina Intermediate School, the Lahaina Boys & Girls Club, the Leialii Hawaiian Homelands, two of the Lahaina wastewater pump stations, the Opukea Townhomes, Lahaina Skate Park, the Lahaina Recreation Center, and the Maria Lanakila Catholic Church. The samples were tested for 16 metals—including the metals that were found at high levels in the ash.
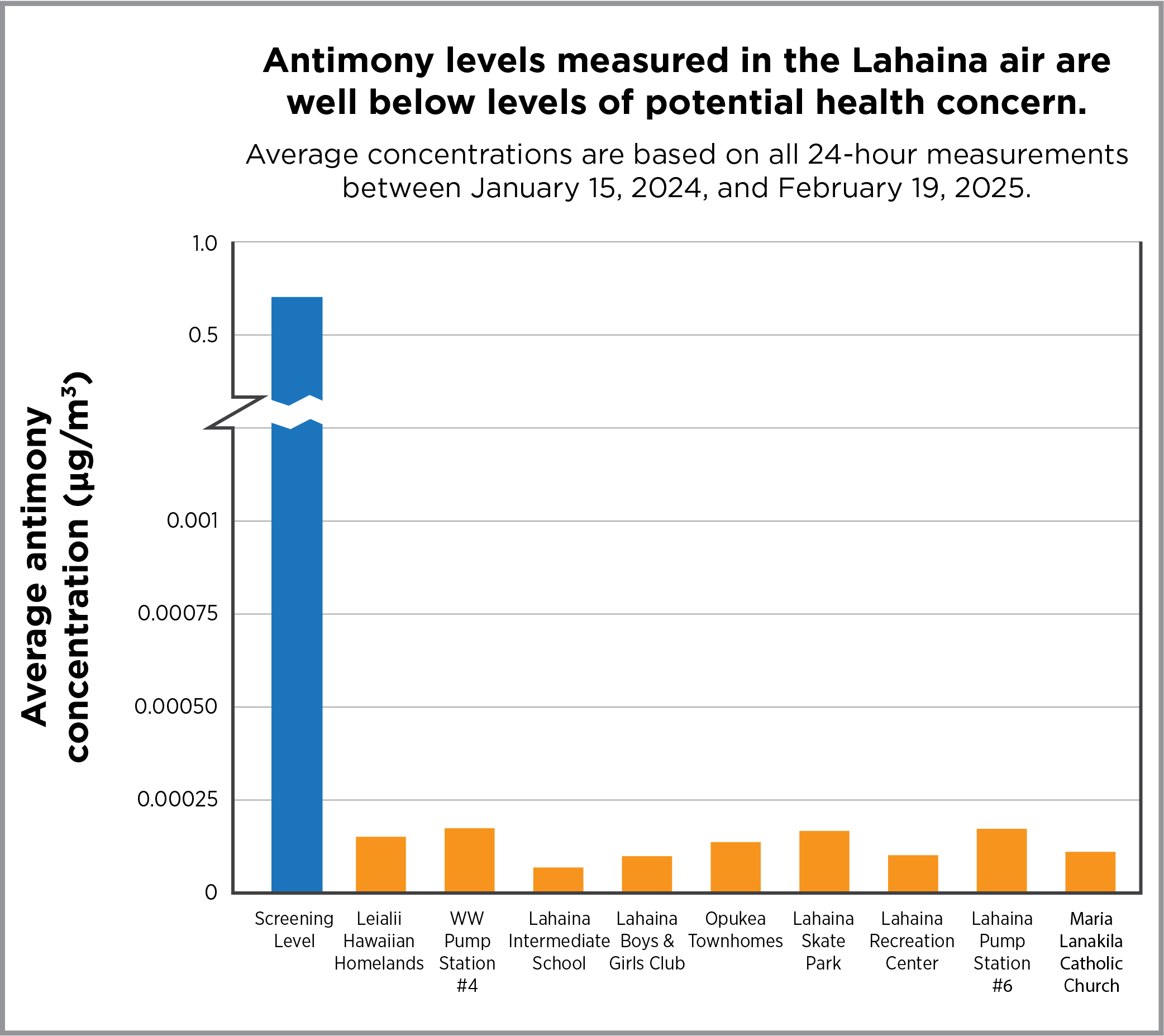
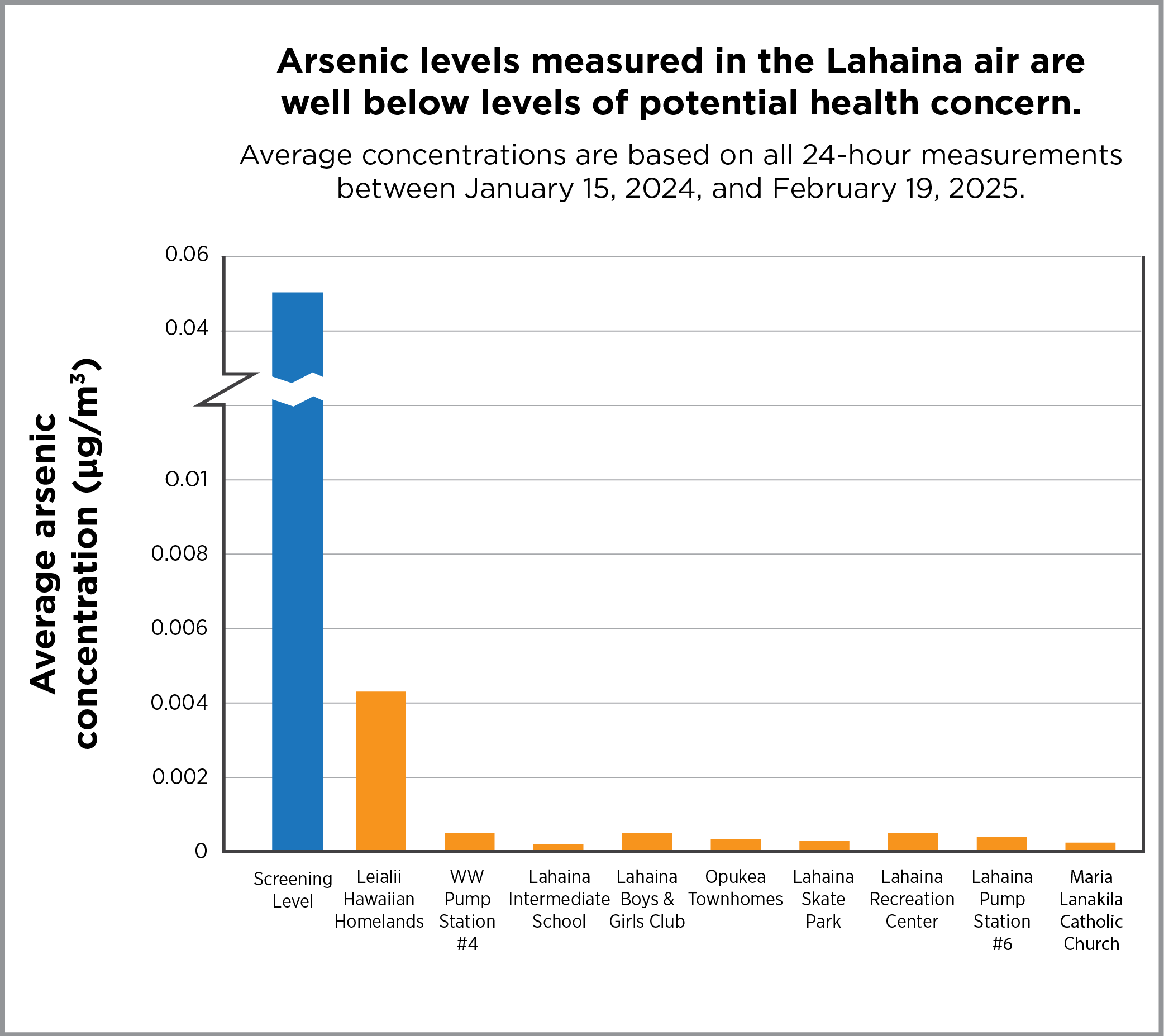
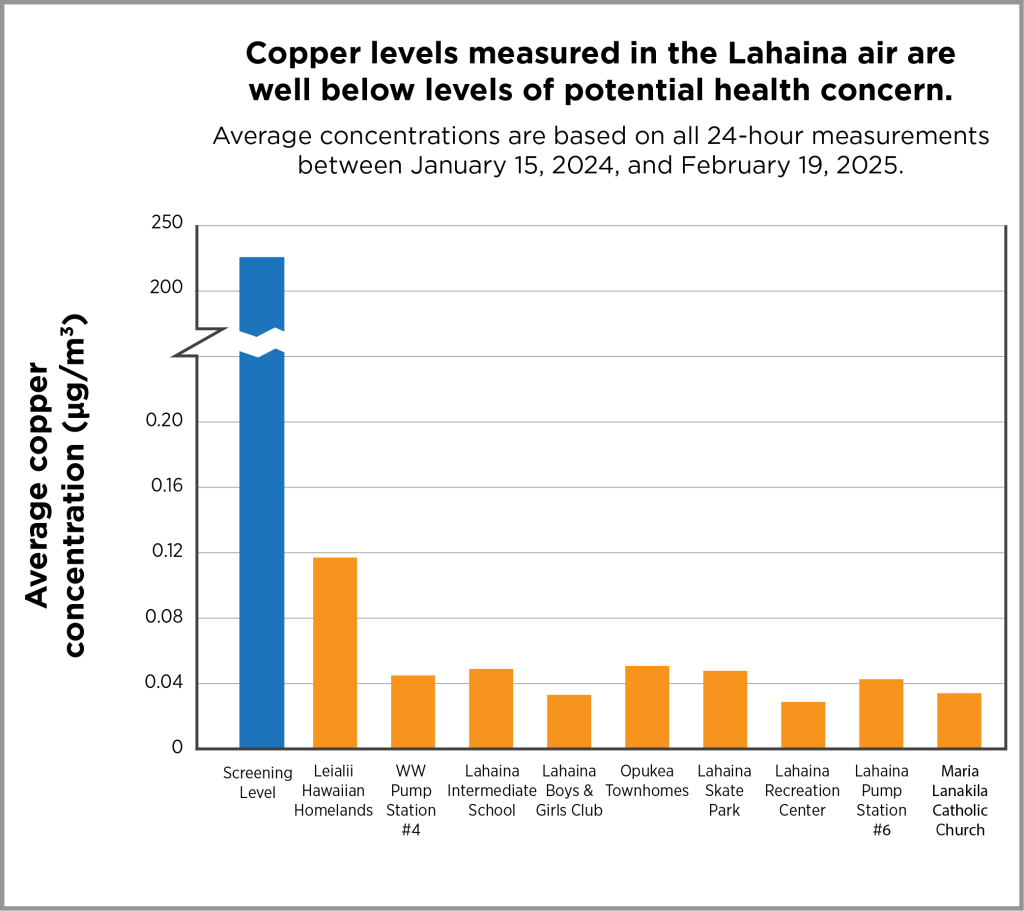
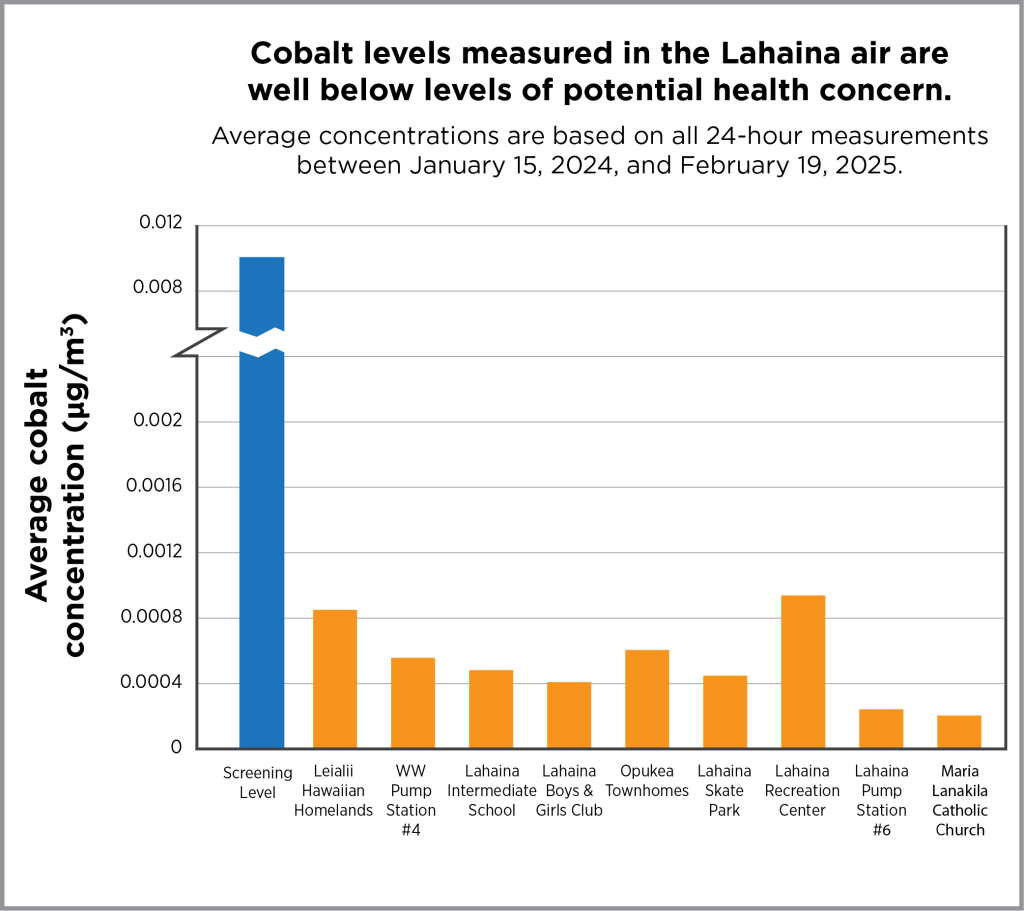
With two exceptions, all samples showed measurements that were extremely low and below levels that are protective of public health. The exceptions were from air samples taken on August 25, 2024, at Opukea Townhomes and the pump station. At the Opukea site, air concentrations of manganese and nickel were greater than levels set to protect public health; and at the Lahaina wastewater pump station, the air concentration of manganese was above the level set to protect public health. The cause of these higher air concentrations is unclear, because no debris removal crews were observed working in the area on that day. Windy weather conditions and factors such as grinding or cutting metal and use of fertilizers at nearby locations could have contributed to these short-lived, elevated air quality impacts.
The section below describes air sampling results for the five metals that DOH previously reported as being at elevated levels in Lahaina ash.
Findings for Antimony (Sb), Arsenic (As), Cobalt (Co), Copper (Cu), and Lead (Pb)
Antimony, arsenic, cobalt, copper, and lead are harmful substances that occur naturally in rock and soils in Hawaii and elsewhere. These substances are also found in a wide range of consumer products and structural materials. After the wildfires burned in Lahaina, these harmful substances were detected in the ash. At high levels of exposure over long time frames, breathing in these substances can cause a range of non-cancer health effects. For some of these substances, like arsenic, longer term exposure at high levels can cause cancer.
Health Findings
Even though the ash in Lahaina contains these five metals, and these same metals have been found in the air, more than 1,000 air samples collected since the wildfires show that the amounts of these metals in the air are extremely low and not harmful to people’s health. USACE has sampled air (PDF, opens in a new tab) at its worksites in and near Lahaina, and their measurements are all below occupational exposure limits.
Recommendation to residents
Continue to protect yourself from harmful substances in ash. If you are near a location where there is visible dust or if the ash will be disturbed, you can limit the amount of metals you might breathe in by either temporarily leaving the area or by wearing a snug-fitting dust mask or N95 mask—look for the words “NIOSH Approved” printed on the mask. Read more about how to protect yourself in DOH’s Maui Wildfires Air Quality Guide for Particle Pollution fact sheet (PDF, opens in a new tab).
What is being done to reduce exposures to metals
Many steps have been taken to make sure no one is exposed to unhealthy levels of metals. Soiltac® has been sprayed on the ash to keep it in place, and debris removal and PDS/TDS Site operations use various strategies—like water sprays—to control dust and keep ash out of the air. DOH reviews the air sample results as soon as they are available to make sure the metals in the air do not reach unhealthy levels and will continue to do so as monitoring takes place for debris transfer from the TDS Site to the PDS.
Air | Ash and Debris | Beach Sand | Coastal Sediment | Coastal Waters | County Parks | West Maui TDS Site | Soil