Checking & Controlling Blood Pressure
WHAT IS BLOOD PRESSURE?
Blood pressure is a measure of the strength of blood pushing against the sides of the blood vessels in the circulatory system. Having high blood pressure is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Blood pressure is measured with two numbers. The top number, called systolic blood pressure, measures the pressure in the blood vessels when the heart beats. The bottom number, called diastolic blood pressure, measures the pressure in the blood vessels when the heart is at rest between beats. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of Mercury (mm Hg).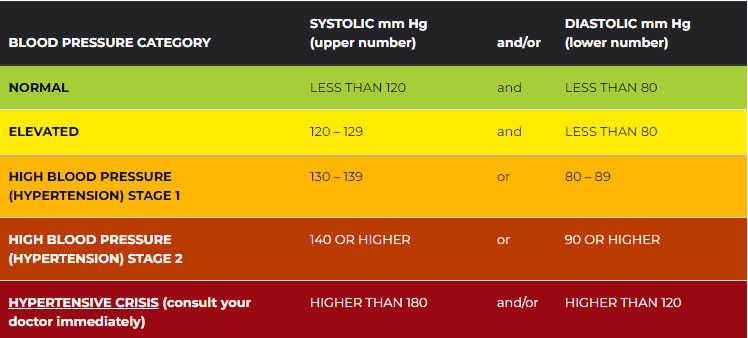
Monitoring Your Blood Pressure at Home
Measuring blood pressure regularly is the only way to know if blood pressure is high. At-home blood pressure machines are available at local pharmacies and retailers for purchase. There are also blood pressure machines available at pharmacies that can be used by patrons.
The American Heart Association recommends using an automatic, cuff-style, bicep (upper arm) monitor to measure blood pressure at home. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice or find options at validatebp.org.
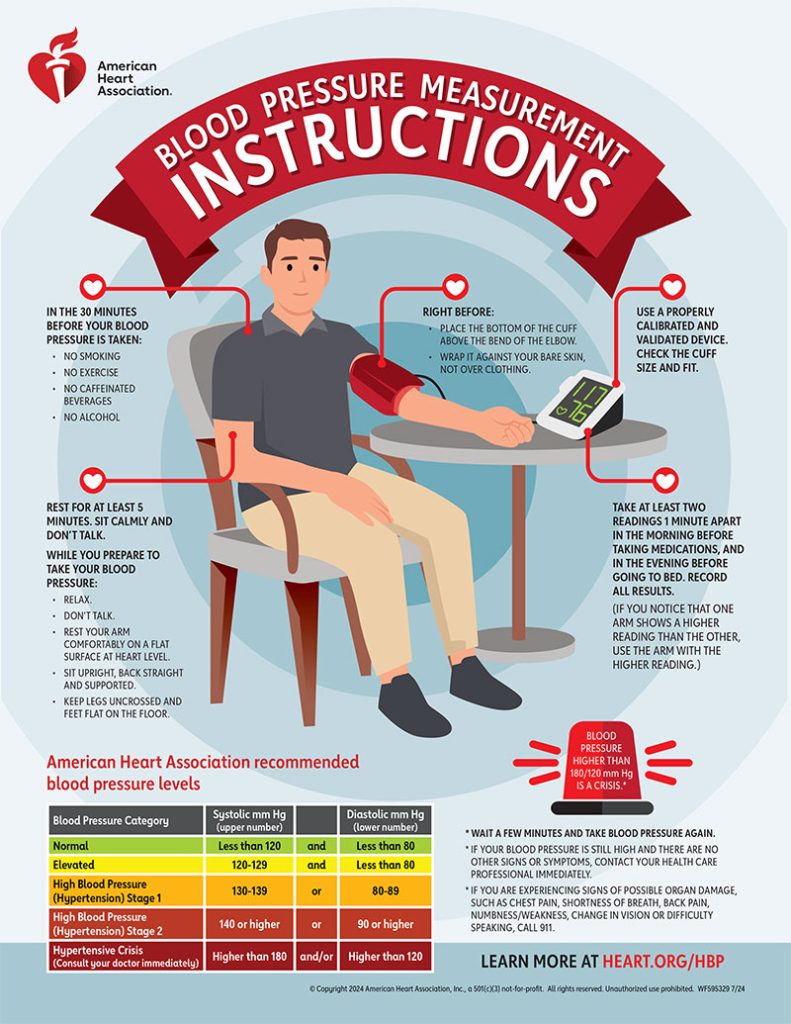
When you are ready to take your blood pressure:
- Rest. Do not smoke, drink caffeine or exercise within 30 minutes of measurement.
Sit correctly. Sit in a chair with both feet flat on the floor. Sit next to a table to let your arm rest while you take your measurement. - Put on the cuff. Remove any tight clothing and place the cuff snugly around the upper part of your bare arm. The center of the cuff should sit over the artery.
- Be consistent. Take your blood pressure at the same time each day.
- Take multiple readings and record the results. Take two or three readings one minute apart, record the results, and share this at your next physician visit. If your monitor has built-in memory to store your readings, take it with you to your appointments. Some monitors may also allow you to upload your readings to a secure website after you register your profile.
- Don’t take your measurements over clothes.
- Record your results. Take two or three readings each time you take your blood pressure and record your results. Be sure to take your results to your next doctor’s appointment.
CONTROLLING YOUR BLOOD PRESSURE
Although we cannot control our genetics, age, race or gender, there are ways to manage and control blood pressure. Lifestyle changes and/or prescribed medications can help to keep blood pressure in check and lower the risk of experiencing the harmful effects of high blood pressure.
If you have been diagnosed with high blood pressure, your doctor may prescribe medication to help control it. Take your medication as instructed and do not stop taking your medication until you talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
- Eat a well-balanced diet low in salt
- Limit alcohol
- Enjoy regular physical activity
- Manage stress
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Quit smoking
- Take your medications properly
- Work together with your doctor



