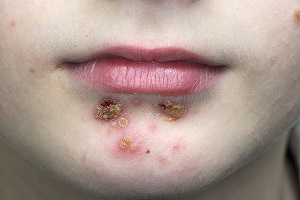
Impetigo
About This Disease
Impetigo is a skin infection caused by bacteria. It is usually caused by staphylococcal (staph) bacteria, but it can also be caused by streptococcal (strep) bacteria. It is most common in children between the ages of two and six. It usually starts when bacteria get into a break in the skin, such as a cut, scratch, or insect bite.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms start with red or pimple-like sores surrounded by red skin. These sores can be anywhere, but usually they occur on your face, arms and legs. The sores fill with pus, then break open after a few days and form a thick crust. They are often itchy, but scratching them can spread the sores.
Transmission
Impetigo can spread by contact with sores or nasal discharge from an infected person.
Diagnosis
Doctors usually diagnose impetigo by looking at the distinctive sores. Lab tests generally aren’t necessary.
Treatment
You can treat impetigo with antibiotics.
Risk in Hawaii
Anyone can get impetigo. Although impetigo is a year-round disease, it occurs most often during the warm weather months. There are more than 3 million cases of impetigo in the United States every year.
Prevention
The bacteria that cause impetigo thrive in breaks in the skin. Simple cleanliness and prompt attention to minor wounds will do much to prevent impetigo. Avoid touching objects that someone with impetigo has used, such as utensils, towels, sheets, clothing and toys. If you have impetigo, keep your fingernails short so the bacteria can’t live under your nails and spread.
Additional Resources
Hawaii State Department of Health Impetigo Factsheet (PDF)
How to Treat Impetigo and Control this Common Skin Infection
See the CDC for more information.